
Contents
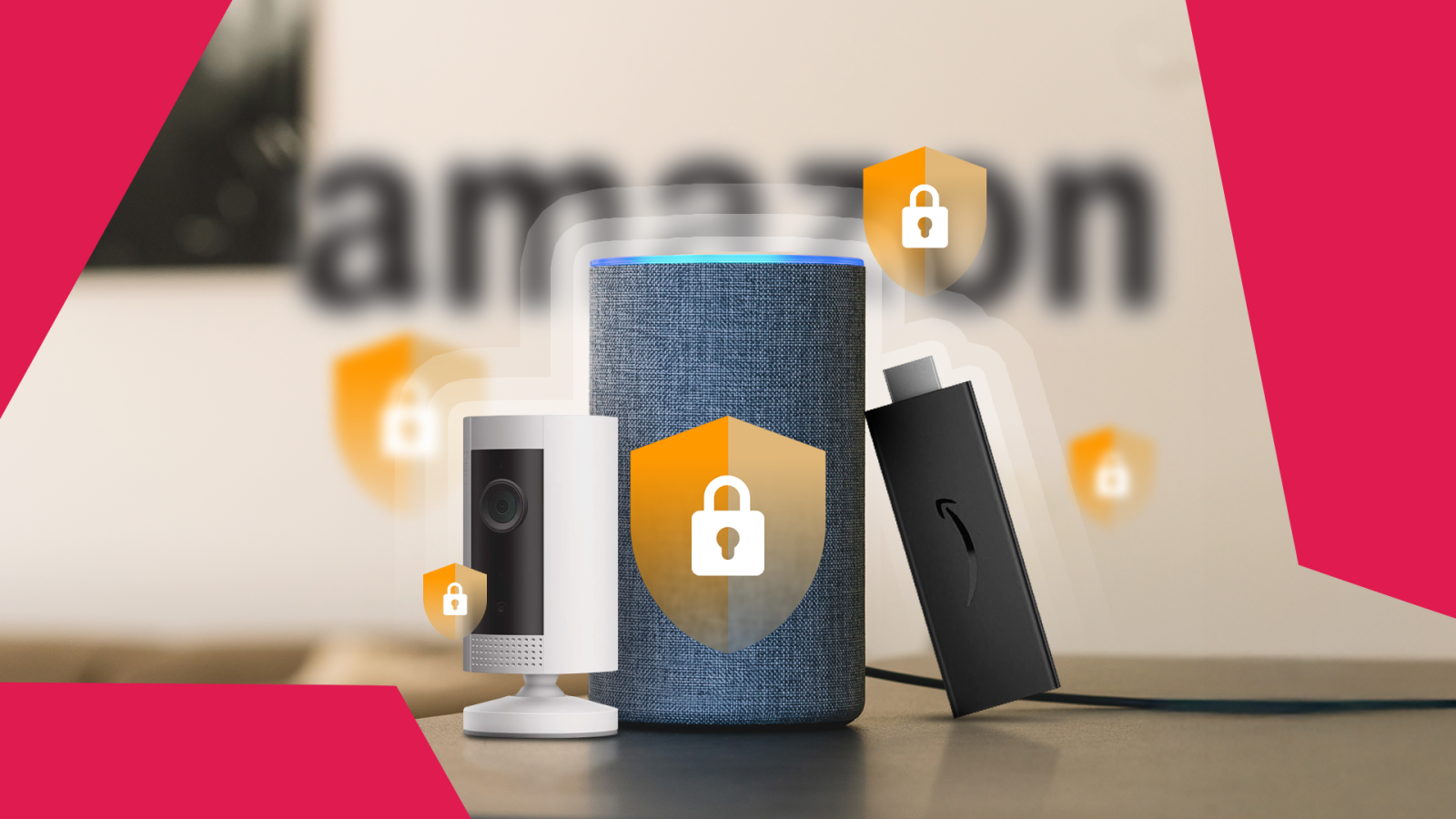
You’d be surprised how much of your home life runs through your Amazon devices. From asking Alexa to play music to checking your Ring Battery Doorbell or turning on smart lights, it’s convenient, but that convenience comes with risks. If you’re not careful, someone could listen in, watch, or make purchases using your voice. That’s why you should take a few minutes to check key privacy and security settings. In this guide, I walk you through the important ones to lock down your account and devices.

Related
8 ways to secure your smart home from hackers
A smart home is only as smart as its security
10 Every Amazon account needs a strong password and 2FA
Don’t let your Amazon account be the weak link

Your Amazon account links your Alexa and Ring devices. If someone gains access, they can make unauthorized purchases or harvest personal data. Past incidents show that weak account security allowed hackers to take over Ring cameras and harass families.
Set a strong, unique password and activate two-factor authentication (2FA). If your password is stolen or guessed, 2FA stops intruders by requiring a verification code from your phone or authenticator app.

Related
9 times it’s smarter to use an authenticator app instead of SMS codes
SMS codes can slip through the cracks, but authenticator apps lock things down tight
9 Remove old devices from your Amazon account
Secondhand gear shouldn’t have first-class access

Every Echo speaker, Fire TV, Ring camera, or device linked to your Amazon account is a potential access point. A device you gave a relative or replaced can remain logged in to your account. A stranger with a secondhand device can access your Amazon account if you don’t deregister it. Remove devices you no longer use. This prevents unwanted people from listening in, viewing your information, or making purchases.
Alexa doesn’t know your kids aren’t shopping pros

Alexa’s voice purchasing feature lets anyone who speaks to Alexa buy items from Amazon with a voice command. That convenience can be risky. If you leave it unrestricted, anyone within earshot of your Echo can order items on your account. Children accidentally buy toys and treats when Alexa processes their requests. Turn off voice purchasing or verify orders with a four-digit PIN. With a PIN, Alexa asks for the code when you initiate a purchase.
7 Manage Alexa’s voice recording privacy and protect your audio from misuse
Alexa remembers more than you think

Alexa constantly listens for the wake word and records your voice commands for Amazon’s cloud. Amazon saves recordings and transcripts indefinitely to improve Alexa’s understanding. Over time, this builds a repository of personal audio data, including sensitive or accidentally recorded conversations.
Storing voice history raises privacy concerns. If your account is compromised, outsiders can access these recordings. Delete your record history or set recordings to delete automatically after a period. Turn off saving them, or opt out of letting Amazon use your voice snippets to improve its services.
6 Turn off Amazon Sidewalk and keep your smart home network private
Keep your signal and data close to home

Amazon Sidewalk shares part of your internet connection with nearby Sidewalk devices. It creates a mesh network. For example, if your neighbor’s Echo falls outside their Wi-Fi range, it can use part of your connection (and you use part of theirs) to stay online.
This can improve reliability, share your bandwidth, and extend your devices into a mesh network beyond your home. Sidewalk is activated by default. Amazon uses encryption and limits Sidewalk data to about 500 MB per month. Still, you may not want your devices to communicate with unknown devices. Deactivating Sidewalk keeps your smart home network closed and private.

Related
9 ways to tell if someone is stealing your Wi-Fi
Netflix buffering? Maybe your neighbor’s streaming, too
5 Restrict Alexa’s Drop In feature and stop surprise audio visits via Alexa
Surprise calls? Not in this house

Alexa’s Drop In feature lets authorized users connect to an Echo’s microphone and speaker to talk. Drop In can be helpful for room-to-room conversations within your household. It poses a privacy risk if unrestricted. If you allow Drop In from contacts, anyone you authorize can appear unannounced on your Echo. After you approve a contact’s Drop In, they can reconnect anytime without approval. You hear a chime, but you may not notice it. Families should limit or deactivate the Drop In.
4 Review Alexa skills and limit their access and permissions
Not all skills deserve access to your data

Alexa Skills acts like an app, extending Alexa’s features with trivia games, smart home integrations, and news updates. Third-party developers create many skills. Activating a skill can grant it access to data or devices. For example, a skill can request your device list, zip code, and phone number. Over time, you accumulate skills you no longer use.
Each activated skill can pose a privacy risk or security weak point, especially those from unknown developers. In rare cases, malicious or poorly designed skills can misuse data. Amazon reviews skills, but you should remain cautious. Regularly audit your active skills and their permissions. Alexa’s Manage Skill Permissions setting lets you review and revoke a skill’s access to your address, profile information, contacts, and more.
Ring’s eyes should only report to you

If your smart home includes Ring doorbells or cameras, secure the videos they record to protect your privacy. Ring encrypts videos in transit and stores them in the cloud, but standard encryption lets Ring or anyone with system access view your recordings. Ring introduced End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) to give users more control.
The E2EE feature encrypts videos using a key you only hold, so you can only decrypt and view them. Ring and Amazon can’t unlock those videos on their servers. E2EE boosts privacy. Even if someone hacked Ring’s cloud or an employee misused access, the videos remain gibberish without your key.
2 Adjust audio and privacy zones on Ring cameras
Black out what doesn’t need to be seen

Source: Ring
Ring cameras capture video of your surroundings and audio of nearby sounds. Recording neighbors or public streets raises privacy and legal concerns. Ring provides Privacy Zones and an Audio toggle to manage this. Privacy Zones let you black out areas in the camera’s view, so the camera ignores and excludes them from the footage.
For example, you could block out a neighbor’s window. Turn off the audio if you don’t need to record porch conversations. That ensures any recorded or shared video contains no sound. Configuring these settings protects privacy and limits the capture of sensitive content. These settings are crucial when cameras monitor semi-private spaces.
1 Use a guest network to isolate smart devices
One Wi-Fi for your laptop, one for Alexa

Image Source: Netgear
Connecting smart home devices to a separate guest Wi-Fi network secures your digital life. IoT devices attract cyberattacks. Placing them on an isolated network reduces the risk of an attack spreading. The attacker stays trapped within the guest network. They cannot move laterally to access your sensitive data.
This segmentation limits a breach’s impact and protects your main network. Most routers let you create a guest network with minimal setup. Ensure it is password-protected and lacks access to local network resources. Name it something neutral, like Guest_WiFi_2G. Use strong router credentials and firmware updates to create a layered defense for your smart home.
Make the most of Amazon devices without the risk
Amazon devices have many features to make your life easier, but that should not cost you peace of mind. Amazon provides these options. Activating them is up to you. Families, in particular, have much to gain from these tweaks. You’ll worry less about what the kids might accidentally do, who might be listening or watching, or how your data is handled.
What’s your reaction?
Love0
Sad0
Happy0
Sleepy0
Angry0
Dead0
Wink0









Leave a Reply
View Comments